On Monday, February 3, 2025, global financial markets experienced significant volatility following President Donald Trump’s announcement of new tariffs on imports from Canada, Mexico, and China. The initial declaration led to sharp declines across major stock indices, reflecting investor concerns over potential disruptions to global trade and economic growth.
The Dow Jones Industrial Average plunged by over 560 points in early trading, while the S&P 500 and Nasdaq Composite each fell by more than 1%. These declines were mirrored in international markets, with European indices such as Germany’s DAX and France’s CAC 40 dropping by approximately 2%. Asian markets also faced downturns, with Japan’s Nikkei 225 losing nearly 3% amid fears of an escalating trade war.
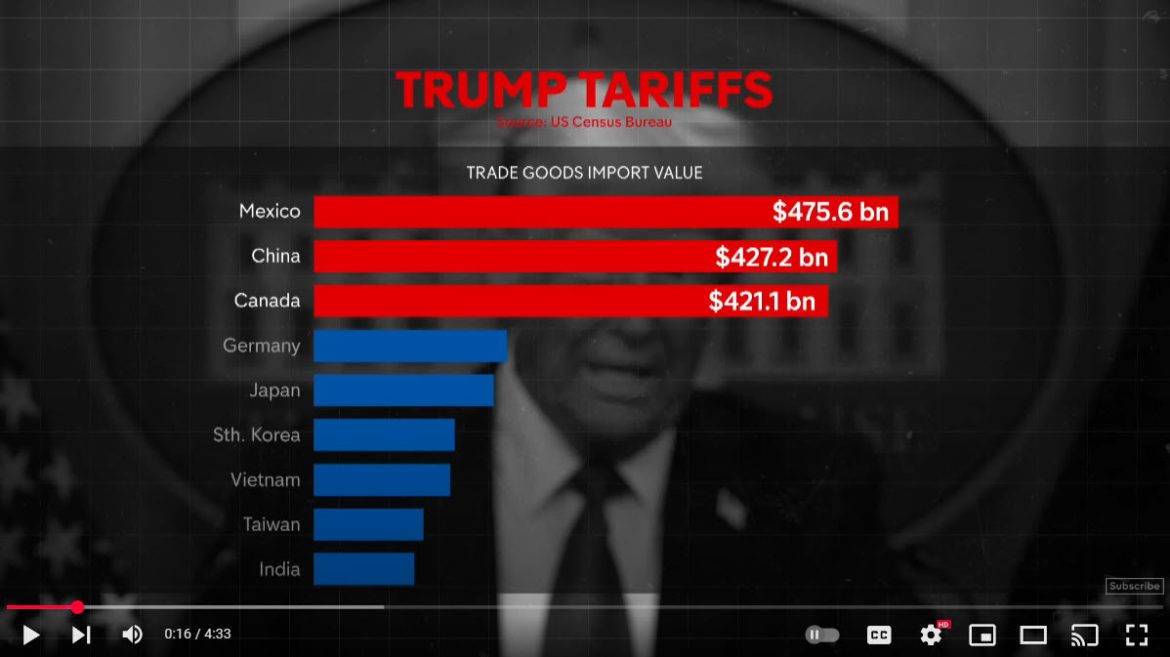
The newly imposed tariffs include a 25% levy on goods from Canada and Mexico, and a 10% tariff on Chinese imports. In response, Canada and China announced retaliatory measures, further intensifying concerns about a full-scale trade conflict. Investors are particularly worried about the potential for these actions to disrupt global supply chains and contribute to rising inflation.
However, market sentiment shifted later in the day after President Trump announced a one-month delay in implementing the tariffs on Mexican goods. This decision followed discussions with Mexican President Claudia Sheinbaum, during which Mexico agreed to deploy 10,000 National Guard members to its northern border to combat drug trafficking into the United States. The postponement provided temporary relief to investors, leading to a partial recovery in stock prices.
Despite the rebound, financial analysts caution that the situation remains fluid, with the potential for further market instability as developments unfold. The tariffs on Canadian and Chinese goods are still scheduled to take effect shortly after midnight, and the possibility of additional retaliatory actions by affected countries adds to the uncertainty.
Economists warn that prolonged trade tensions could have adverse effects on the global economy, including slower growth and increased inflationary pressures. Businesses and consumers alike may face higher costs as tariffs raise the prices of imported goods, potentially leading to decreased spending and investment.
In the financial markets, sectors with significant exposure to international trade, such as technology and manufacturing, experienced notable declines. Companies like Nvidia saw their stock prices drop by over 5%, while major European carmakers, including Volkswagen and BMW, faced losses between 5% and 6%. Commodities were also affected, with oil prices initially rising due to supply concerns before stabilizing later in the day.
As the situation evolves, investors are advised to monitor developments closely and consider the potential impacts on their portfolios. The interplay between trade policies, corporate earnings, and economic indicators will be critical in shaping market dynamics in the coming weeks.